|
Information
for structures design
|
|
that
will be galvanized
|
|
|
|
When
designing or fabricating steel, there are often certain
requirements one must consider. Hot-dip
galvanized steel has its own set of design and fabrication
considerations one should be familiar with before the start of
the project. Incorporating the design and fabrication
recommendations will help ensure the best quality coating and
most successful project. The design and fabrication
considerations for hot-dip galvanizing differ from other
coatings, but are simple to follow once you become familiar with
them.
|
|
|
|
Whether
designing a galvanized project for the first time, or the 100th
time, the key component to a successful project is communication
between the architect, engineer, fabricator and galvanizer.
Opening the lines of communication early in the design and
fabrication process can eliminate potential costly pitfalls later
in the process
.
|
|
|
|
When designing a structure to be galvanized, it must be considered that the pieces will be submerged in molten zinc at a temperature of 450°C.
|
|
|
|
General principles for tubular structures
|
|
|
|
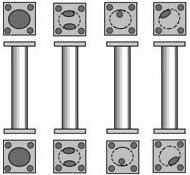
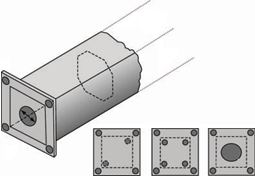
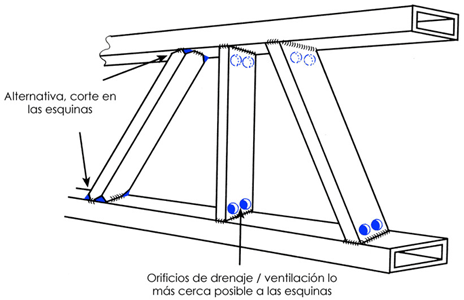
ALL tubular structures must have ventilation and drainage holes and these must be as wide as possible with a minimum of Ø12mm.
The measurements of the holes, preferably, will be 25% of the internal diameter. This percentage can be influenced by the shape of the structure, it is recommended to consult with the galvanizer
|
|
|
|
|
Sections of sealed tubes with plates. Preferably
the holes should be located diagonally opposite at the ends.
|
|
|
|
|
|
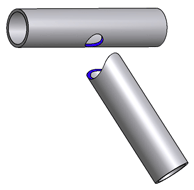
With the tubular welded structures, the sections must be interconnected by means of oblique joints or with drilled holes. Here are some examples.
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Threaded
parts
|
|
|
|
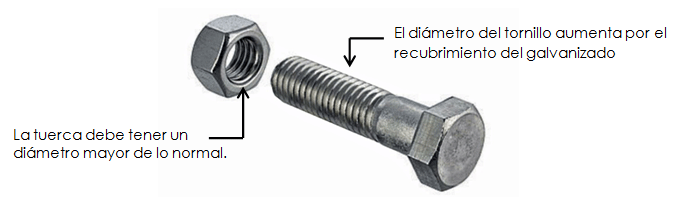
When manufacturing and / or galvanizing threaded rods and screws, the corresponding standard nominal diameter (unmodified) must be maintained. On the contrary, the nominal internal diameter of the nuts must be modified and made slightly larger and then reviewed after being hot-dip galvanized. Consult our manual for the design of parts to obtain more information about the over-dimensioning of the nuts.
|
|
|
|
|
|
Ventilation, filling and drainage
|
|
|
|
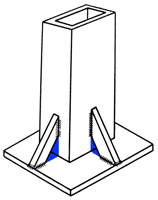
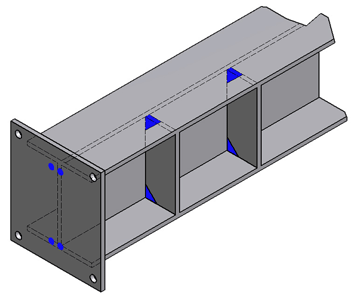
The assemblies and structures with internal and external reinforcements, they should cut the intersecting corners. The spaces created should be the largest possible without compromising the structural strength, to help the fluid of the molten zinc and to prevent the accumulation of air and ash generated by the same galvanized. |
|
|
|
 |
|
|
|
|
Welded parts |
|
The welds should be continuous. Welding slag (arc welding with coated electrode) can not be easily removed with acid cleaning, so it must be removed before galvanizing.
Gas protected arc welding (MIG or TIG) is preferred, as this method results in a slag that is easy to clean by acids.
In case of welds at the ends, this should be continuous all around the piece to prevent unnecessary penetration of acid into the cracks. |
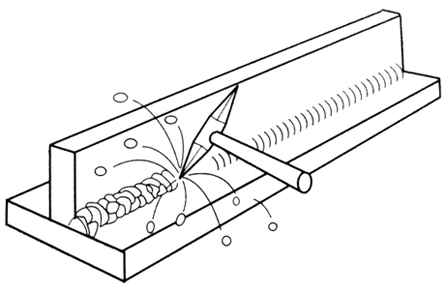
|
|
|
|
Other recommendations:
|
|
|
|
No parts or marks of paint or any type of coating (such as enamels) are allowed on the parts to be galvanized. |

|
|
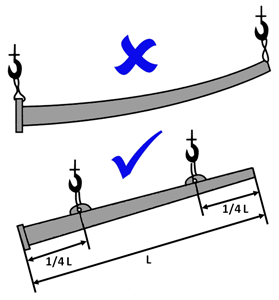
|
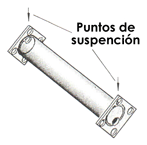
The best way to hold a long structure is 1/4 of its total length at both ends. |
|
|
| |
| |
|

|
Download our Design Manual here, with more details on the guidelines that should be considered to manufacture structures that are going to be galvanized.

|
|
|
|